Overview
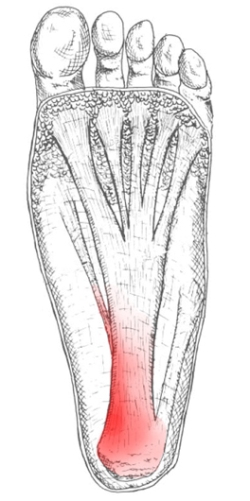
Plantar fasciitis is the pain caused by degenerative irritation at the insertion of the plantar fascia on the medial process of the calcaneal tuberosity. The pain may be substantial, resulting in the alteration of daily activities. Various terms have been used to describe plantar fasciitis, including jogger’s heel, tennis heel, policeman’s heel, and even gonorrheal heel. Although a misnomer, this condition is sometimes referred to as heel spurs by the general public.
Causes
Because the plantar fascia supports your foot and gets used every time you take a step, it has to absorb a large amount of stress and weight. If too much pressure is put on the plantar fascia, the fibers can become damaged or start to tear. The body responds by causing inflammation in the affected area. This is what causes the pain and stiffness of plantar fasciitis. Things that can increase the risk of plantar fasciitis include tight calf muscles. Tight calves make it harder to flex your foot, and this puts more stress on the plantar fascia. Weight. Carrying a few extra pounds puts added pressure on your feet every time you take a step. Activities that put a lot of stress on the feet. This includes things like running, hiking, dancing, and aerobics. Bad shoes. Footwear that doesn’t give your foot the support it needs increases your risk of plantar fasciitis. You’ll want to ditch any shoes that have thin soles or inadequate arch support, or ones that don’t fit your feet properly. Routinely wearing high heels can also cause your Achilles tendon to contract over time, making it harder to flex your foot. Jobs that involve a lot of standing or walking on hard surfaces. Jobs that keep you on your feet all day, like waiting tables or working in a store, can cause damage to your plantar fascia. High arches, flat feet, or other foot problems. The shape of your foot can affect the way your weight is distributed on your feet when you stand. If weight distribution is a bit off, it can add to a person’s risk of plantar fasciitis. How someone walks can increase the stress on certain parts of the foot too.
Symptoms
Most people with plantar fasciitis have pain when they take their first steps after they get out of bed or sit for a long time. You may have less stiffness and pain after you take a few steps. But your foot may hurt more as the day goes on. It may hurt the most when you climb stairs or after you stand for a long time. If you have foot pain at night, you may have a different problem, such as arthritis , or a nerve problem such as tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can usually diagnose plantar fasciitis just by talking to you and examining your feet. Rarely, tests are needed if the diagnosis is uncertain or to rule out other possible causes of heel pain. These can include X-rays of the heel or an ultrasound scan of the fascia. An ultrasound scan usually shows thickening and swelling of the fascia in plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you protect your injured plantar fascia appropriately the injured tissues will heal. Inflammed structures will settle when protected from additional damage, which can help you avoid long-standing degenerative changes. Plantar fasciitis may take from several weeks (through to many months) to heal while we await Mother Nature to form and mature the new scar tissue, which takes at least six weeks. During this time period you should be aiming to optimally remould your scar tissue to prevent a poorly formed scar that may become lumpy or potentially re-tear in the future. It is important to lengthen and orientate your healing scar tissue via massage, gentle stretches, and light active exercises. In most cases, your physiotherapist will identify stiff joints within your foot and ankle complex that they will need to loosen to help you avoid plantar fascia overstress.A sign that you may have a stiff ankle joint can be a limited range of ankle bend during a squat manoeuvre. Your physiotherapist will guide you.

Surgical Treatment
The most common surgical procedure for plantar fasciitis is plantar fascia release. It involves surgical removal of a part from the plantar fascia ligament which will relieve the inflammation and reduce the tension. Plantar fascia release is either an open surgery or endoscopic surgery (insertion of special surgical instruments through small incisions). While both methods are performed under local anesthesia the open procedure may take more time to recover. Other surgical procedures can be used as well but they are rarely an option. Complications of plantar fasciitis surgery are rare but they are not impossible. All types of plantar fasciitis surgery pose a risk of infection, nerve damage, and anesthesia related complications including systemic toxicity, and persistence or worsening of heel pain.